- Bookmarks and command/directory history functions implemented - Function to edit commandline with $EDITOR - Faster git parser |
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| fish_greeting.fish | ||
| fish_prompt.fish | ||
| fish_right_prompt.fish | ||
| README.md | ||
budspencer theme
Translation of zsh's prezto budspencer theme. This theme is
optimized for visibility and a fast workflow.
Requirements
Non standard tools:
- xsel
- git
Configuration
The theme behaves similar to vim's airline/powerline plugins. Thus, it needs a
powerline font. Although it works with emacs mode, it's more powerful
with vi mode. In order to enable vi mode, put the following lines into
$HOME/.config/fish/config.fish before set fish_path $HOME/.oh-my-fish:
set -U fish_key_bindings fish_vi_key_bindings
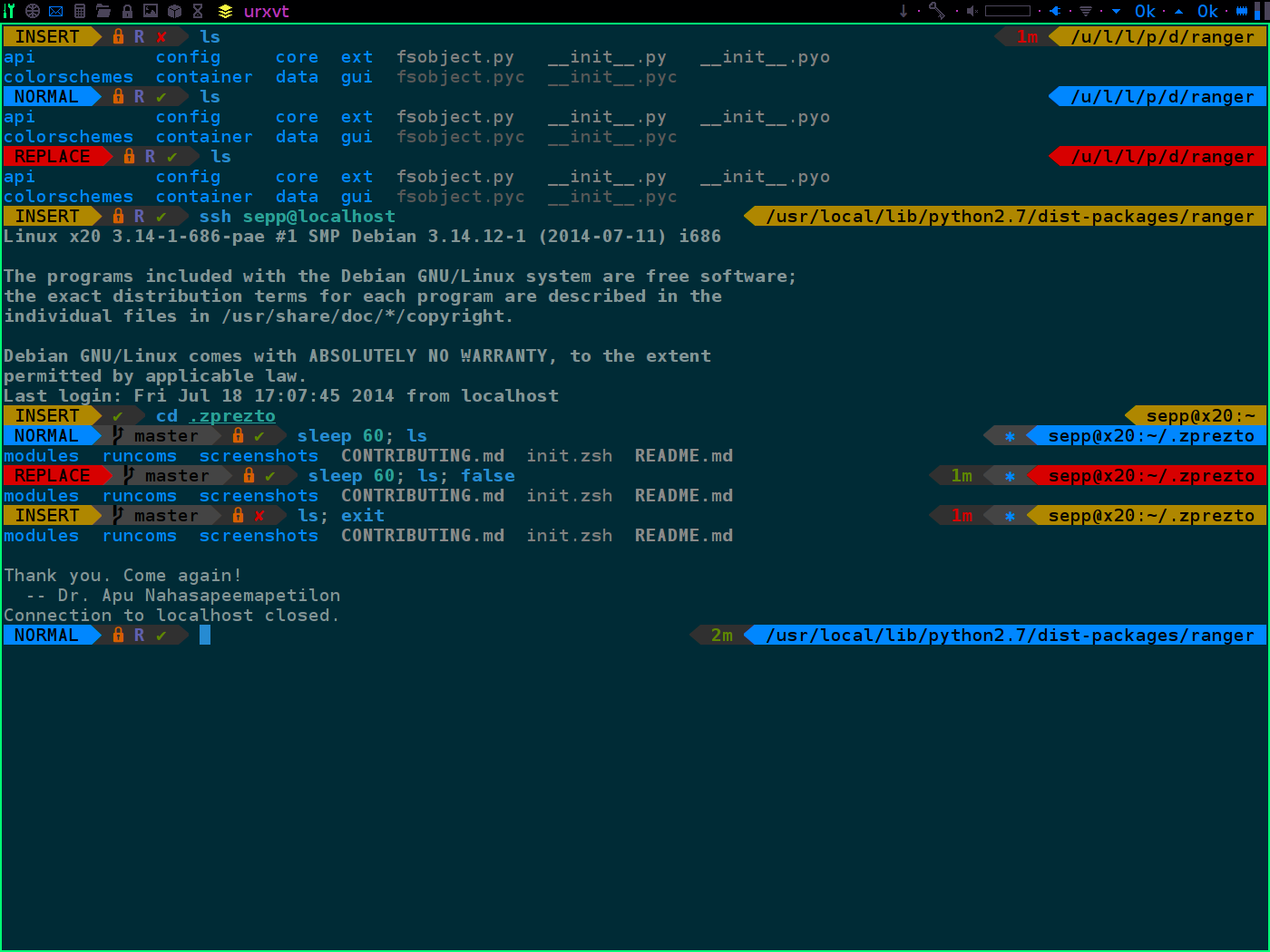
Left prompt segments
- Vi mode indicator similar to vim airline/powerline, cursor color also changes
if terminal supports it - Git repository information
- Status symbols
- ⌘: present working directory is in bookmark list, can be toggled with
#to
show the number of the bookmark - V: vi is parent process
- R: ranger is parent process
- ⚙: there are background jobs, can be toggled with
#to show the amount of
background jobs - : no write permissions in present working directory
- ✔: last command succeeded, can be toggled with
#to show the status value - ✘: last command failed, can be toggled with
#to show the status value - ⚡: superuser indicator
- ⌘: present working directory is in bookmark list, can be toggled with
- Present working directory
Right prompt segments
- Last command's duration time
- Git status
- symbols:
- ↑: git repository is ahead origin
- ↓: git repository is behind origin
- +: changes have been added to git index
- –: files have been deleted in work tree
- ✱: files have been modified in work tree
- →: files have been renamed in git index
- ═: there are unmerged commits
- ●: there are untracked (new) files
- ✭: there are stashed commits
- symbols:
Toggle prompt segments
The following shortcuts need vi-mode:
-
Style of "present working directory"-segment can be toggled in NORMAL and in
VISUAL mode with space bar- styles implemented:
short(shows username, short hostname and truncated path; recommended in
most cases)long(shows username, full hostname and full path; useful for copy-paste
in ssh connections)none(shows nothing except small delimiter; useful for small terminals)- If prompt is toggled with
#, the IP address is shown instead of the
hostname.
- configurable by global list
$PWDSTYLE(if not set, defaults to
short long none); putset -g PWDSTYLE none longinto
$HOME/.config/fish/budspencer_config.fishif you want to toggle only between
noneandlong.
- styles implemented:
-
Style of symbols can be toggled in NORMAL and in VISUAL mode with
#- styles implemented:
symbols(shows status symbols)numbers(shows numbers instead of symbols in left prompt as well as amount of changes in
right git prompt)
- styles implemented:
Quickly navigate in history of working directories
There is a function d that shows the history as enumerated list. Unlike
fish's builtin dirh, d does not show any duplicates. Enter a number to jump
to a directory within the list. It's also possible to give that number directly as
argument to the d function.
The following shortcuts need vi-mode:
- Press
Hin NORMAL mode to change present working directory to previous
working directory in history. - Press
Lin NORMAL mode to change present working directory to next working
directory in history.
Quickly navigate in command history
The function c shows the command history as enumerated list equivalently to
the d function. Selections are also paste into the X clipboard.
Bookmarks
A bookmark can be created with mark. It can be removed with unmark.
Bookmarks are persistent and universal.
They are stored in $HOME/.config/fish/budspencer_config.fish.
A new shell automatically changes working directory on startup to newest bookmark.
m is a function that shows the bookmarks as enumerated list equivalently to d.
The following shortcuts need vi mode:
- Create a bookmark for present working directory with
min NORMAL mode. - Remove a bookmark for present working directory with
Min NORMAL mode.
Edit commandline with your favorite editor
The function edit-commandline let you edit the commandline with your editor.
It makes your commandline as powerful as your editor. If $EDITOR is not set,
use vi.
The following shortcut needs vi mode:
- Type
.in NORMAL mode to edit commandline in editor.
Screenshot
TODO
- vi REPLACE mode, as soon as REPLACE mode is implemented within fish